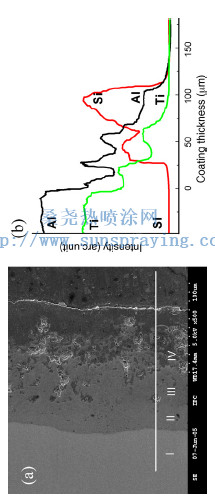
TiAl alloys attracted more attention in many fields due to their high specific strength, high melting point and excellent corrosion resistance, such as important parts of rocket, automobile, aeroplane and space shuttle. However, many properties of TiAl alloy should been further promoted in most of applied fields. A series of surface modification techniques, such as ion implantation, titanizing, and MCrAlY composite coating have been developed to improve properties of TiAl alloys. Microarc oxidation (MAO) is a distinguished technique to fabricate a ceramic coating on light alloys due to the following advantages: (a) an excellent adhesion between coating and substrate because of in situ growth of ceramic coating, as metal ions coming from substrate and oxygen ions coming from electrolyte; (b) low cost, as this technique has no need of costly vacuum or gas shielding conditions; (c) easy controlling for processing, as coating can be easy controlled by electronic parameters and composition of electrolyte; (d) friendly for environment, as alkaline electrolytes were employed in the process. Especially, MAO method enabling to achieve more thick ceramic coatings with high hardness, good wear resistance has shown a widely applied prospect. At present, many papers about MAO were focused on the treatments of Al, Ti and Mg. However, few data can be available concerning on fabricating the ceramic coatings on TiAl alloys by microarc oxidation technique. Specially, no paper has been reported on tribological properties and corrosion resistance of MAO coating on TiAl substrate. In this work, structure and composition of MAO coatings on TiAl alloy were analyzed, and tribological and corrosive behaviors of the coatings were evaluated. Microarc oxidation is an advanced method to fabricate ceramic coatings on valve metals. The coatings up to 110 m thick were prepared on TiAl alloy by the alternating-current microarc oxidation in silicate electrolyte. Their structures, composition, wear resistance and corrosion resistance were evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), ball-disc dry sliding and electrochemical polarization tests. Results showed that the dense layer of coatings was mainly composed of Al2TiO5 and TiO2 rutile phases, while the loose layer contained a large amount of amorphous SiO2 besides Al2TiO5 and TiO2 rutile phases. Maximum value of microhardness in the coating was about three times higher than that of TiAl substrate. The wear rate of coating was only 1/10 of TiAl substrate. Corrosion current density of the coated TiAl alloy was greatly reduced. The microarc oxidation is a promising method to improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of TiAl alloy.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

