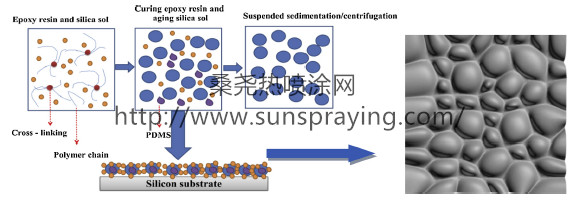
As a kind of thermosetting resin, epoxy resins in a variety of media have great chemical stability and processing performance. However, the three-dimensional network structure makes EP material bearing decentralized stress capacity poor, so wearing in the friction condition is severe. Over the past decade, many studies have been carried out to solve these problems by using different flexible materials as a mesophase for physical blending or chemical reactions. The modified materials fall into four types: thermoplastic terminating functional groups, reactive liquid rubbers, organic-inorganic hybrid materials and reactive toughness diluents. The organic-inorganic hybrid materials are the most widely used. Various nano-fillers or reinforcing fibers are commonly used in the study to modify the epoxy resin. Preparation of EP composites with higher friction properties, for example, solid lubricants and nano-sized inorganic particles can have a synergistic effect in the dry conditions to improve the tribological properties of EP. The effect of nanoparticles is due to "rolling effect". Friction process can be transferred to form a transfer film, reducing the friction coefficient. Reinforcing fibers can relieve stress concentration during the process of friction, and inhibiting layer is formed to protect the materials. Enhancing the hydrophobic properties of the material is conducive to accelerating the formation of material suppression layer. The recent rise of using lubricating oil combined with solid lubricants has become a research hotspot. However, solid-liquid two-phase combination is more difficult. Lots of researches focus on the adsorption of lubricating oil by porous self-lubricating materials. While it’s evident that this method has certain flaws, such as the large amount of water absorption and high water absorption of porous materials, at the same time, it is difficult to store them at high temperature. In complex conditions, severe oil contamination and wearing are difficult to deal with. The aim of this study is to investigate the direct interaction of silica sol into epoxy curing molecules based on sol-gel, and that of participating in the curing reaction. A micro bead structure is prepared. Micro bead structure is characterized by a small surface tension, at the same time in the friction process, it will produce rolling effect and scattered concentrated stress. The formation of microspheres promotes the surface abundance, resulting in a more obvious micro-nano structure, increasing the hydrophobicity of the material. When the applied load exceeds the load capacity of the microbeads, the beads will be fragmenting and the internal polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) will be released to form an oil lubricating film. As the friction process progresses, the oil film gradually accumulates. With the change of friction mode, the friction can be further reduced. And the bearing capacity of which is the switch of oil releasing in the material. The sequent works are mainly the design and manufacture of different strength beads. Use varying workloads in various conditions to obtain different lubrication effects. This study focuses on this point and provides great help for the subsequent preparation of intelligent bearing lubrication materials. A heat- and wear-resistant superhy drophobic coating containing epoxy resin microspheres was designed on the basis of sol-gel method. The epoxy resin- silica sol (EPS) composites were obtained from phase separation, using silica sol as the dispersant, and epoxy-amino as curing system. In this process, the pale-yellow EPS/polyamide (PA) solution turned turbid and formed suspension. The synthesis of epoxy resin microspheres generated two layer structure. Epoxy microspheres were observed on the surface of the EPS by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The curing time of EPS composites was an important condition for obtaining films with good overall properties. However, the prepared EPS/PA composites were poor at wear-resistance. When continuing to use carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as a nano-reinforced phase, the formation of micro-nano rough surface intensified material itself scrolling effect to further improve the wear resistance and mechanical stability of composites. It was observed that the thermal stability of the material itself was improved compared with that of EPS. In the test of dynamic friction and hydrophobic performance, it can be found that the mechanical stability of the material itself had also improved. Its mechanical oscillation frequency range narrowed, resulting in reduced wear and increased wear resistance.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

