In recent years, there has been increased interest in the research and development of metal matrix composite coatings (MMCs) due to their expected engineering applications. These composite coatings can impart functional properties such as wear, corrosion and oxidation resistance, dispersion hardening or self-lubrication relative to pure metal, so that they can protect the metal substrates more effectively against severe environments during operation. The properties of MMCs depend on the contributions from the distributed and matrix phases. They can be produced through a number of routes including metal processing, powder metallurgy, and electrodeposition techniques. The codeposition of fine ceramic or polymer particles in a metal matrix can be achieved by an electrodeposition technique, which is a single step, low-temperature process that results in nanocomposite coatings wherein the matrix or the particles can be in nanosize or both can be in nanosize. The nickel matrix prepared by electrodeposition has been widely used in the chemical, mechanical and electronic industries because of their wear, corrosion and oxidation resistance. They find application as coatings of engine cylinders, high-pressure valves and dies and in the production of musical instruments, drill fittings, car accessories and small aircraft and electro-technical parts.One of the continuing goals of the nanocomposite coatings is the production of economically viable coatings with enhanced properties such as higher microhardness and corrosion, oxidation and wear resistance. There are reports on the synthesis and properties of various composite coatings such as Ni–SiC, Ni–Si3N4, Ni–Al2O3, Ni–ZrO2, Ni–CeO2, Ni–TiO2, Ni–La2O3, Ni–CNT, Ni–diamond and Ni–microcapsules. Among these, Ni–SiC is the most widely used wear resistant composite coating on the trochoid of Wankel engines. SiC powder is relatively expensive (15$ for 250 g) and its preparation involves multi-steps and high temperature calcinations. In the search for inexpensive and readily available ceramic particles, pumice stone seemed to be attractive. Pumice stone is basically an alumino-silicate, has a Knoop hardness of 705, is very cheap (1$ for 250 g) and readily available and is actually a kind of glass. It is used in precast masonry units, poured concrete, insulation and acoustic tile, and plaster. It is also used as an abrasive in polishes, pencil erasers, cosmetic exfoliants, toothpastes and the production of printed circuit boards. Pumice is a light, porous igneous volcanic rock. It has a porous structure and a large surface area and it can be processed easily. The use of pumice as an adsorbent to remove metals from wastewater treatment at low cost is a wellestablished process. Pumice has been found to be effective for the removal of phosphate ions from water and is used as an additive for cement. However, there are no reports on the synthesis and properties of Ni composite coating containing pumice particles.
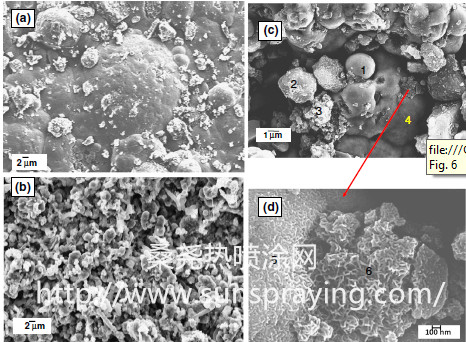
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

