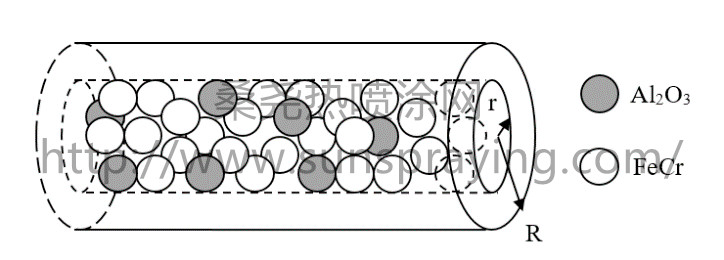
Different methods are used for working surface treatment in order to extending the life of machine details subjected to wear. One of the most effective methods is the deposition of flux-cored wires, see Student et al. (1994) or Li et al. (2014) or Shapovalov et al. (2017) or Zhang et al. (2019). Deposition of coatings from the Fe–Cr system is used extensively for protection from wear, increase the strength and hardness of the treated surfaces. The use of flux-cored wires makes it possible to vary widely the composition of the sprayed coatings. In addition, these coatings have high resistance to wear by Vinokurov et al (2009, 2011). Heating of the powder material during arc metallization is carried out due to the heat released as a result of the influence of electric current between the wire elements. Arc metallization is a procedure of layer-by-layer application to heated metal products of small thickness. The height of the electric arc is minimal, and the molten wire is dispersed by a gas flow directed along the axis of the filler material. Various additives are used to improve the quality of the coating. Corundum particles were used as a strengthening additive in the present study, Al2O3 particles exhibit high hardness, wear resistance and thermal stability. The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of the arc metallization on the microstructure of the wire sprayed coatings. Meanwhile, the content of the corundum in the obtained coatings depending on the current strength were investigated. As a research material, a FeCr cored wire with refractory additives of corundum Al2O3 by Bolotina N.P. et al. (1995) was chosen. The cored wire with a diameter of 2 mm was manufactured by EDU-500 equipment at Scientific and Production Co. Ltd, "VEKHA-1" (Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Russia). The outer shell of wire was stainless steel. The filling material was mixed of ferrochrome and aluminum oxide powders with the following composition, % wt.: C ~0,47 – 0.51; Cr ~2 – 4; Al2O3 ~10 – 15; Fe – other. The entry of ferrochrome and aluminum oxides increases the hardness and strength of wear-resistant coatings, see Lin et al. (2014) or Yasir et al. (2015) or Guo et al. (2016). The filling factor of the cored wires was 31% . The coatings were applied to the side surface of the wear test discs with a diameter of 50 mm and height of 10 mm with the help of an industrial electric arc metallization unit EDU-500C under the technological conditions listed in Table 1 with the deposition distance of 130 mm. The microstructure of powder coatings obtained after different technological modes was studied using AXIO Observer D1m "Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH" optical microscope. The morphology of coatings were observed by using scanning electron microscope (SEM, HITACHI-TM 3030) equipped with the EDS analyzer (XFlash 6 "Bruker"). The powder wire with fireproof additives has been carried out. One of the most promising high-energy methods of application of wear-resistant coatings is electric arc metallization wires, the use of the powder wires for the restoration of worn parts of equipment gives unparalleled flexibility in choice of coating material and in coatings with a variety of properties – high hardness and wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high heat resistance and heat resistance and etc. Coatings of about 300μm thickness were prepared through high temperature fusing of a powder wires on steel substrate. Corundum particles were used as a strengthening additive, Al2O3 particles exhibit high hardness, good wear resistance and thermal stability. The microstructure and morphology of the wear-resistant coatings were investigated. It is shown that the thickness of the deposited layers in the coating does not depend on the change in the magnitude of the current. The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of the arc metallization on the microstructure of the wire sprayed coatings. Meanwhile, the distribution of chemical elements in obtained coatings were investigated. In addition we found the dependence of the corundum content in the wire thermal spray coatings.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

