Heretofore, there are few literature and patents reported on the water-based BSLCs with excellent mechanical and tribological properties, which can be attributed into the following reasons. Firstly, there is a significant gap in the bonding capacity and wear resistance between the water-based resin and the organic-solvent-based resin; secondly, the typical solid lubricants and nano-fillers have poor water dispersibility; thirdly, the matching design between the components in the coating is difficult to regulate. Firstly, it is pointed out that, compared with common water-based epoxy resins, water-based acrylic resins, water-based polyurethane resins and other resins, water-based polyamideimide (PAI) resin exhibits the following advantages: (I) water-based PAI resin can be dispersed with water in any ratio to form a uniform and stable water system; (II) wide temperature range, dimensional stability and creep resistance, etc.; (III) high bonding strength, high adhesion to metal materials, excellent mechanical properties (hardness, adhesion, toughness and impact strength). Accordingly, it possesses significant scientific value to take water-based PAI resin as the binder to prepare the water-based BSLCs. Secondly, graphite, has excellent friction-reducing properties and chemical stability, and is relatively inexpensive. Additionally, based on the preliminary inquiry, the water-dispersibility of graphite particles are optimized by virtue of appropriate surface treatment methods, and the appearance, mechanical and tribological performances of the water-based PAI-graphite BSLCs have been improved to some extents. Nevertheless, there is still a certain gap concerning the mechanical strength and wear resistance between the water-based PAIgraphite BSLCs and organic-solvent-based BSLCs, consequently, the further optimization of the matching design between the components in the water-based PAI-graphite BSLCs is urgently needed. The purposes of the work are to fabricate novel environment-friendly water-based polyamide-imide (PAI)-graphite- LaF3 bonded solid-lubricating coatings (BSLCs), and investigate the corresponding tribological properties and mechanisms. The experimental results reveal that the preparation of the water-based PAI-graphite-LaF3 BSLCs has significantly reduced the usage of organic solvent. When the mass percent of nano-LaF3 is 5 wt%, the water-based PAI-graphite-LaF3 BSLCs exhibit superior mechanical and tribological properties, which are comparable to those of the reported organic-solvent-based BSLCs. The tribological mechanisms were systematically investigated concerning the failure mechanism, the tribological reactions and structural fluctuations of graphite.
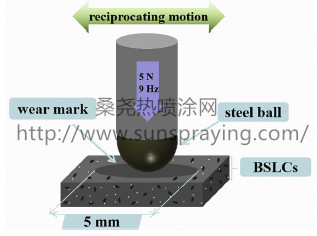
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

