Wear often leads to the failure of mechanical parts. One of the effective means of controlling wear is the deposition of wear resistant coatings on the mechanical parts. Thermal spray techniques are often used to deposit thick ceramic coatings due to its high-temperature characteristics. Plasma spraying has been selected for this study because it is one of the most important technologies used in various industries to deposit wear resistant oxide coatings. Plasma sprayed Al2O3/TiO2 coatings are proved to have outstanding wear properties which has been qualified for use in a number of shipboard and submarine applications. And it is also widely used in equipment remanufacturing, aerospace industry, light industry and automobile industry. To meet the requirements of extreme and demanding tribological applications, nanostructured Al2O3/TiO2 coatings have been developed. Compared with conventional coatings, thermal sprayed nanostructured Al2O3/TiO2 coatings show unique and superior properties such as high hardness, good wear resistance and excellent thermal shock resistance due to a retained nanostructure, especially with partial melting of the nanostructured powders. Graphene is a two-dimensional nano-layered structure of carbon atoms, with ultra-thin thickness, excellent mechanical properties that are superior to other carbon allotropes. Graphene shows great lubricity and relatively high wear resistance. So it is often used as a reinforcing phase to enhance the tribological properties of the material. Graphene can improve the toughness and wear resistance of bulk ceramic materials. It also has favorable effects on the properties of ceramic coatings. Li et al. improved the tribological properties of ZrO2 and CaSiO3 ceramic coatings by using 1 wt% Graphene nanosheets (GNs) as reinforcing agents respectively. Gómez et al. observed that the addition of 0 wt%, 1.2 wt% and 2.3 wt% graphene nanosheets (GNPs) to the Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 coatings reduced the steady-state friction coefficient and wear volume. Bian et al. added graphene to the chemically bonded phosphate ceramic coatings and studied the role of graphene dispersion in enhancing the wear resistance. With the introduction of GNPs, wear significantly reduced due to the improvement of the mechanical properties and the smoother wear surface. Furthermore the GNP detached from the substrate and adhered to the worn surface forming an adherent lubricating film, resulting in a decrease in the coefficient of friction. Qin et al. studied the preparation of Al2O3 coatings by using a mixture of 0.2 wt% Graphene and 0.2 wt% carbon nanotubes as reinforcements. The results showed that compared with the pure Al2O3 coating, the wear depth and width of the composite coating were much lower. Graphene modified nanostructured Al2O3/TiO2 coatings were prepared on 316L stainless steel by plasma spraying. The microstructure of feedstocks and coatings was characterized using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The bonding strength of the coatings was studied by dual tensile tests. The Vickers hardness of the coatings was used in this paper. The wear resistance of the coatings was demonstrated by sliding wear tests. The coatings containing 6 wt% graphene shows excellent wear resistance, of which the porosity is 35% lower, the bonding strength is 62% higher, and the wear rate is 20–25% lower than that of the non-graphene coatings. In addition, there is no obvious effect on the hardness of the coatings with the addition of graphene.
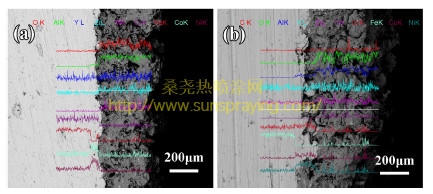
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

