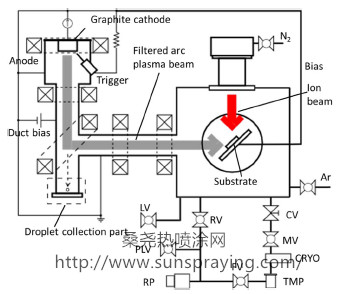
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings have been widely used in the field of machine components due to their attractive properties including chemical inertness, high hardness, and wear and corrosion resistance. Among various kinds of DLC, carbon nitride (CNx) has got rising interest since the prediction that a β-C3N4 compound could have similar properties as diamond with even higher hardness . Although until now the ideal structural CNx has not been successfully synthesized, numbers of groups have attempted to fabricate CNx with various methods, such as reactive magnetron sputtering, ion beam deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (CVD), pulsed laser deposition (PLD), and filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA). Meanwhile, previous researchers observed the excellent tribological properties for CNx coatings. Wang et al. have reported the low friction of self-mated CNx coatings in inert gas environment due to the sp2 rich carbon tribolayer. Zhou clarified the wear mechanism of amorphous CNx sliding against Si3N4 balls in water. CNx coating is also suitable for the actual application of mechanical sliding parts under oil lubrication. Wäsche et al. have reported a-CNx coatings with the N-content of 0–28 at% have a large variation of hardness from 8.02GPa to 16.97 GPa, and exhibit the lowest friction coefficient and the wear rate under paraffin oil lubrication compared to those in dry air and humid air. Chen et al. have found the CNx films exhibit very low friction coefficients of 0.042–0.070 under wet lubrication in oil, which is much improved from stainless steel and TiN film. In Chen's study, a-CNx films synthesized using magnetron sputtering also present good wear resistance under mineral oil lubrication. Based on the tribological performance of CNx coatings under oil lubrication, the low friction coefficient could be attributed to C=N bonds in the coatings, while the wear mechanism is mainly abrasive wear as the high hardness of CNx compared to the counter body. With lubricant additive in the oil, the dangling bonds of CNx coatings, as the oiliness agent adsorption sites, strongly determine the low friction and wear behavior. However, according to the previous studies, amorphous CNx coatings with markedly low friction in oil lubrication still show low hardness and durability, which might limit the mechanical application. For this purpose, nitrogen is doped into tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C), high sp3-bonded DLC (up to 80%), to synthesize tetrahedral amorphous carbon nitride (ta-CNx) by FCVA, as FCVA is effective with highly ionized plasma of energetic carbon ions among all the deposition methods. Tetrahedral amorphous carbon nitride (ta-CNx) is suitable for tribological application due to its excellent mechanical and adhesion properties. In this study, ta-CNx coatings with N/C ratios (0–11%) are deposited by ion beam assisted filtered arc deposition (IBA-FAD), and the tribological properties are investigated with a ballon- disk tribo-tester. The results show that nitrogen doping decreases the fraction of sp3 bonding, hardness, Young's modulus and roughness. In oil ta-CNx presents slightly decreasing friction coefficient and improving wear resistance with the N/C ratio, indicating softer ta-CNx with better wear resistance. The lower surface roughness after friction of high nitrogen content ta-CNx makes it more likely to transit to mixed lubrication, resulting in lower contact load that can explain the better wear resistance.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

