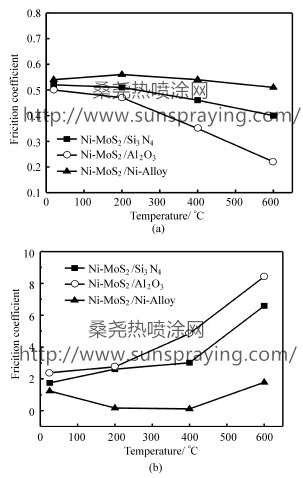
Solid lubricating materials that are effective over an extreme range of operating temperatures are necessary for the development of new generation high-performance gas turbine engines. WU et al prepared Ni/MoS2 self-lubricating composite by powder metallurgy method and found that self-lubricating properties of the composites changed in accordance with the formation situation of the surface lubricating film. Peterson et al. studied the high-temperature friction properties of Ni-Cu-Re alloy and reported that naturally occurring oxide films were responsible for friction reduction at high temperature. Dellacorte investigated friction behavior of Alumina/PS300 and Inconel . Foundation item: National Defense Basic Research Program alloy/ PS300 from 25 ℃ to 600 ℃ and found that the metal counterface generally exhibited lower friction and wear at 25℃ but higher friction and wear at 650 ℃. Many research results indicated that tribological performance of each mating pairs had a relationship with the formation of suitable transfer films. In this paper, nickel-based composites containing molybdenum disulfide were prepared by powder metallurgy (P/M) method. Their mechanical and tribological properties were investigated and effect of counterface on frictional behavior was evaluated. Ni-Cr-W-Al-Ti-MoS2 self-lubricating composites were prepared through the powder metallurgy (P/M) method. Their friction properties were investigated by a pin-on-disk tribometer in the range from the room temperature to 600℃. Alumina, silicon nitride and nickel-iron-sulfide alloys were selected as the counterface materials. Results indicate that the lowest friction coefficients under 0.22 can be obtained at 600 ℃ when rubbed against alumina. When rubbed against nickel-iron-sulfide alloys, are presented the lowest wear rates in the magnitude of 10-6 mm3/N·m, one order of magnitude lower than those when rubbed against ceramics. In the case of three rubbing pairs, the wear rates of the composite containing MoS2 present themselves inversely proportional to friction coefficients. With alumina ceramics used as a counterface, transfer films and glaze layers will form on the contact surface playing a main role in lubrication at high temperatures. However, when silicon nitride and nickel-iron-sulfide alloy are used, the lubricating transfer films appear not to be prominent. Nickel-based self-lubricating composites containing sulfur were prepared by powder metallurgy (P/M). The composites mainly consisted of nickel-based solution, chromium sulfide, tungsten. Alumina ceramic, silicon nitride and nickel-iron-sulfide alloy were selected as counter materials, the lowest friction coefficient of 0.22 ~ 0.50 was obtained when using alumina ceramic as counter material, while the lowest wear rates of about 10-6 mm3/N·m were presented with nickeliron- sulfide as counterface.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

