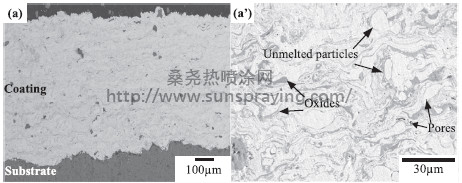
The application of lightweight materials has grown rapidly in the area of transportation including aircrafts, motors and high-speed trains, in order to save energy and achieve high performance. Due to the low density, good thermal conductivity and machinability, aluminum alloys have been widely used as engine block materials instead of traditional cast iron materials in the passenger cars. However, because of the poor wear resistance of aluminum alloy, low-cost cast iron liners are usually embedded in the aluminum engine cylinders to improve the wear resistance. During the practical operation, the distinct thermal expansion coefficients between cast iron (~12 E-6/K) and aluminum alloys (~23 E-6/K) can result in the loosening of the embedded liners during cyclic heating and cooling processes, which leads to the failure of the engine. In addition, the cast iron liners can further increase the engine weight by about 2 kg per set of four liners. In recent years, there has been a trend to substitute the implantation of cast iron liners with thermal sprayed wear resistant coatings. Several thermal spraying techniques have been used to produce wear resistant coatings on the aluminum engine block materials, including plasma spraying, wire arc spraying and high velocity oxygen fuel spraying. Among them, plasma spraying has advantages of higher jet speed, less oxidation and higher deposition efficiency. Various types of coatings can be made, including metallic coatings, metal matrix composite (MMC) coatings, and ceramic coatings.Owing to the low cost and good mechanical properties, Fe-based powders are the preferred materials for the industrial application of wear protection for various substrate materials . The present study aims to investigate the effect of materials composition on the bonding and wear behaviors of plasma sprayed Fe-based coatings on Al-Si substrate. Three types of powder materials with distinct chemical compositions were used as the source powders, including high chrome steel powder which can improve the oxidation, wear and corrosion resistance of the coatings [18], and Fe-based high chrome and nickel alloyed self-fluxing powder which not only has good wear and corrosion resistance, but also has good fluidity and wettability,and cast iron powder as a comparison material since the traditional cylinder liner is made of cast iron. The microstructure analysis, hardness, bonding and wear tests were performed. The correlation of materials composition, phase transformation, bonding and wear behaviors were discussed to provide an insight view when identifying the suitable coating materials for Al-Si alloy substrate. The quality of plasma sprayed coatings is governed by both bond and wear properties during the service period, associated with a number of factors including substrate surface conditions, materials composition, phase transformation, and etc. In the present study, three different Fe-based powder materials including gray cast iron, high chrome steel and high chrome and nickle contained self-fluxing powders were plasma sprayed onto the Al-Si alloy substrate. The microstructure, hardness, phase composition, bonding strength and wear properties of the deposited coatings were investigated. The XRD results revealed that severe oxidation of gray cast iron coatings occurred during the deposition, while no obvious oxidation and phase transformation were detected for chrome steel coatings after spraying. However, the transition of γ-(Fe, Ni) phase into α-(Fe,Cr) phase was confirmed in the self-fluxing coatings. In addition, the Cr and Ni alloying elements enhanced the diffusion between Fe and Al across the coating-substrate interface. Three types of Fe-based coatings showed improved wear resistance in comparison to Al-Si alloy substrate, in terms of coefficient of friction, mass and volume loss. The chrome steel coatings have better integrated performance of bond strength and wear properties. Distinct wear mechanisms were revealed for three types of coatings, i.e. a mixture of adhesive and abrasive wear for gray cast iron coatings, an oxidation dominant wear for chrome steel coatings, and a mixture of oxidation and fatigue wear for selffluxing coatings.
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

