The acceptance of thermal spray coatings in many applications depends on the effect of the coating on the fatigue performance of the coated part. One of the factors that influences the fatigue life of thermal spray-coated components is the residual stress in the coating. This study investigates the fatigue performance of tungsten carbide–cobalt (WC–Co) thermal spray coating systems. Bending fatigue tests of specimens with WC–Co coatings on both 4130 steel substrates and 6061 aluminum substrates were conducted. The through-thickness residual stress level in the thermal spray coatings was determined using the modified layer removal method. The effect of the residual stresses on the fatigue life of the coated specimens was analyzed. It was found that there is a direct relation between the residual stress in the coating and the fatigue life of the coated part. Fatigue life can be changed by a factor of ten due to the level of compressive residual stress in the coating. The objective of determining the effect of average compressive residual stress of 80 MPa and a specimen coating residual stress on fatigue failure was accomplished with an average coating compressive residual stress of 760 for the constant deflection bend testing of WC–Co coat- MPa was found to have 30 times longer life than a ings on both aluminum and steel substrates. The increase specimen with an average coating compressive residual in the life of the part with higher average coating compresstress of 80 MPa. sive residual stress is demonstrated by the results of these The results of the fatigue tests for the specimens with tests, where the loading is cantilever beam bending. steel substrates are shown in. The maximum applied (a) Increasing the compressive residual stress in the stress in the substrate at the coating / substrate interface WC–Co coating increased the number of cycles to failure versus the log of the number of cycles to failure for the in the 6061 aluminum substrate specimens. shot-peened 4130, the chrome-plated, and the thermal (b) The WC–Co-coated 4130 steel substrate specimens spray-coated specimens is plotted. having a low compressive residual stress had approximate- Examining and comparing the coated materials to ly the same number of cycles to failure as the chromethe chrome-plated material shows that the HVOF WC–Co plated specimens. (c) Increasing the compressive residual stress in the WC–Co coating increased the number of cycles to failure in the specimens with steel substrate. (d) The number of cycles to failure for the WC–Cocoated 4130 steel substrate specimens having a higher compressive residual stress approaches the number of cycles to failure of the bare shot-peened steel. However, other modes of failure not considered in this research occur in coated components, for example, spalling. Increasing the compressive residual stress in the coating beyond some value that has not yet been determined might significantly increase the likelihood of failure by spalling. Fatigue testing using other specimen geometries and loadings, such as uniaxial tension and rotating–bending, is planned. Further testing to determine the relation between. Fatigue life in bending of chrome-plated and thermal spray-coated residual stress levels in the coatings and fatigue life will be specimens on 4130 substrate. conducted.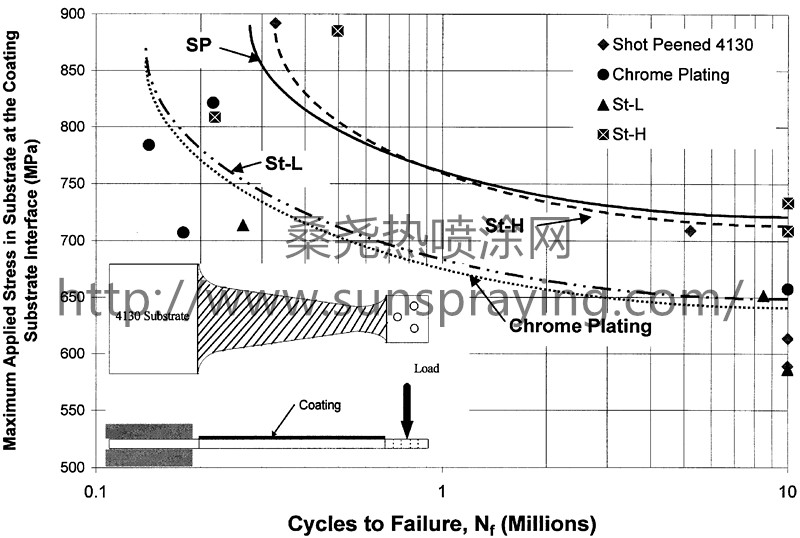
本文由桑尧热喷涂网收集整理。本站文章未经允许不得转载;如欲转载请注明出处,北京桑尧科技开发有限公司网址:http://www.sunspraying.com/
|

